The light sensor is a unique tool that can
come in handy for numerous uses such as measuring objects and detecting
objects. The tool is used in labs for scientists, in offices for the general
work force and in home security systems.
Definition
A
light sensor is a mechanical device sensitive to light, temperature, radiation
level, that transmits a signal to a measuring or control instrument, according
to Dictionary.reference.com.
Similar to how the human eye is sensitive to light
and body hair is sensitive to nearby objects, the light sensor is a tool that
is sensitive.
Function
This
instrument can be used to give information on distance, shape, speed,
dimensions and types of substances contained in various objects, depending on
the area of study it is being used for.
With a high level of precision, they
are used for measuring purposes in architecture and offset printing. (A type of
printing process used by large commercial printers. The ink doesn't press
directly on the paper, it is distributed from a metal plate to a rubber mat
where it then proceeds to the paper.
Proplem Definition
Nobody doubts the important role played by light on crops.
The greenhouse must collect a maximum of sum radiation all day long in winter,
and every morning and every evening all
the year round to get a favourable thermal balance from short IR and allow active
photosynthesis through the “visible” (provided no factor involved in the
process falls down to the minimum, i.e. is missing to a certain extent .
The intensity or the level of light, has a vital effect in
the velocity of the photosynthesis process which is essential to all green plant
, the duration of light, or day length, also has profound photoperiodic
influence; and sources of artificial light, as distinct from sunlight, have
different simulative effects on plants.
Types of artificial lighting are; Tungsten filament,
Discharge lamps, and Fluorescent lamps.
The Effective reflection ensures that the maximum amount of
light is concentrated on mum amount of light is concentrated on the plants
being treated.
The main roles for lighting in greenhouse are:
1-To allow working on short winter days or in the evening.
2-To provide day-length manipulation or night-break
techniques by the use of low intensity tungsten filament lights, suspended
above the plants.
3-To supplement the natural daylight when if falls below at
level sufficient to maintain optimum photosynthetic activity, and to improve
vegetative development and flower truss initiation a high intensity light .
4-To illuminate growing rooms.
How we solve the problem?
We control the light of greenhouse using PIC
microcontroller and light sensor LDR which sense the intensity of light in the
greenhouse and if the light is not enough an external lamp switched on
compensating the low light .
Light
Dependent
Light-dependent sensors are
inexpensive and commonly used for gauging and responding to light levels. These
light sensors work as automatic switches for different devices. They belong to
a group called photoresistors because their resistance increases as light
levels increase, which is why they're commonly present in outdoor lights like
streetlamps. As light levels increase, their resistance increases and turns the
lights off or down.
Why LDR?
·
Automatic Headlight
Dimmer
·
Night Light Control
·
Street Light Control
·
Position Sensor
·
The relation between
LUX and resistance is linear as shown in figure
Algorithm:
1-set the setting point of the light intensity of greenhouse
according to the type of plant on the greenhouse.
2-The sensor contimously sensing the light intensity in the
greenhouse as variation in its resistor.
3-The sensor enter its analog signal to A/D converter.
4-The A/D converts the analog signal into digital signal
giving it to the controller.
5- The controller compare the signal coming from the sensor
with the setting point :
-If the light intensity coming from the sensor is less than the setting point then
Lamp is turned on .
-else
The lamp still off.
How do you connect LDR sensors with a PIC ??
It will not work with
just the LDR. You need to measure voltage at one of the ADC inputs. The voltage
comes from a potential divider made from a fixed resistor and the LDR in series
with the ADC connected to the center. If you omit the fixed resistor the LDR
will pull the PIC input high, even under dark conditions and the ADC will
always read maximum voltage.
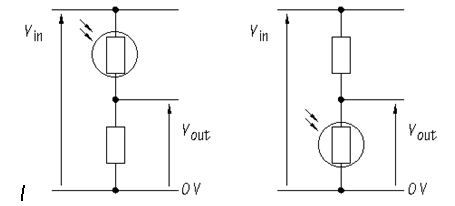
Note that there are two ways you can connect this:
1. LDR goes to the supply, resistor goes to ground.
2. Resistor goes to supply, LDR goes to ground.
Option 1 will give an increasing voltage as it gets brighter but you have to carry the supply line wherever the LDR is mounted. If it shorts to anything you could damage the supply or the wiring.
Note that there are two ways you can connect this:
1. LDR goes to the supply, resistor goes to ground.
2. Resistor goes to supply, LDR goes to ground.
Option 1 will give an increasing voltage as it gets brighter but you have to carry the supply line wherever the LDR is mounted. If it shorts to anything you could damage the supply or the wiring.
Option 2 will give a decreasing voltage as it gets lighter but this is easy to compensate in software. It has the advantage that the LDR is grounded at one end and the resistor limits the current, giving some degree of protection.
The optimum resistor value will give best voltage swing between lightest and darkest conditions. Typically, choose a value equal to the mid way between LDR dark and LDR light resistances.
There are just two
ways of constructing the voltage divider, with the LDR at the top, or with the
LDR at the bottom:
You are going to
investigate the behavior of these two circuits. You will also find out how to
choose a sensible value for the fixed resistor in a voltage divider circuit.
Remember the
formula for calculating Vout :
The block diagram of the light circuit is as the following
 10:00 ص
10:00 ص
 Unknown
Unknown













0 التعليقات:
إرسال تعليق